Laparoscopic Incisional Hernia Surgery In Ahmedabad
Condition
Inguinal hernia occurs when a portion of intestine or abdominal tissue
protrudes through a weakened spot or opening in the abdominal muscles, usually in the groin
area. This can result in a noticeable bulge or lump that may be painful, especially when
bending over, coughing, or lifting heavy objects.
Treatment Options
SURGICAL PROCEDURE
- 1. Watchful Waiting
(Observation): For small, asymptomatic hernias, especially in elderly
patients or those with significant medical comorbidities, a watchful waiting
approach may be considered. This involves monitoring the hernia for any changes and
managing symptoms without immediate surgical intervention.
- 2. Surgery: Most inguinal
hernias require surgical repair to push the protruding tissue back into place and
strengthen the weakened abdominal wall. Surgery is typically recommended to prevent
complications such as incarceration or strangulation, which can lead to serious
health risks.
- Open Repair: Involves making
an incision directly over the hernia, pushing the protruding tissue back into the
abdomen, and then reinforcing the abdominal wall with stitches or mesh
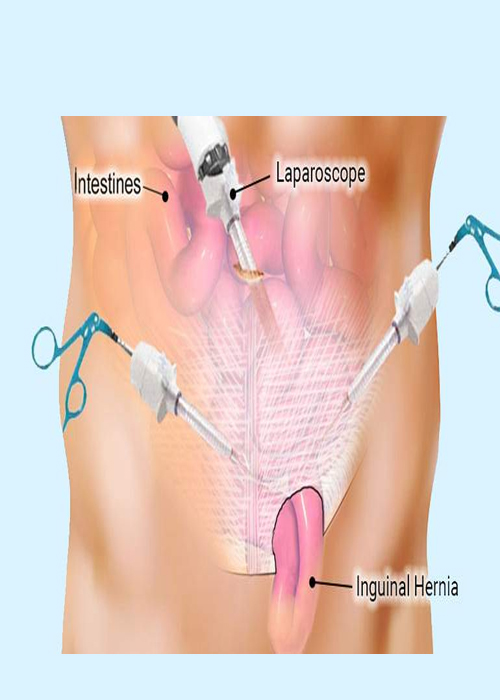
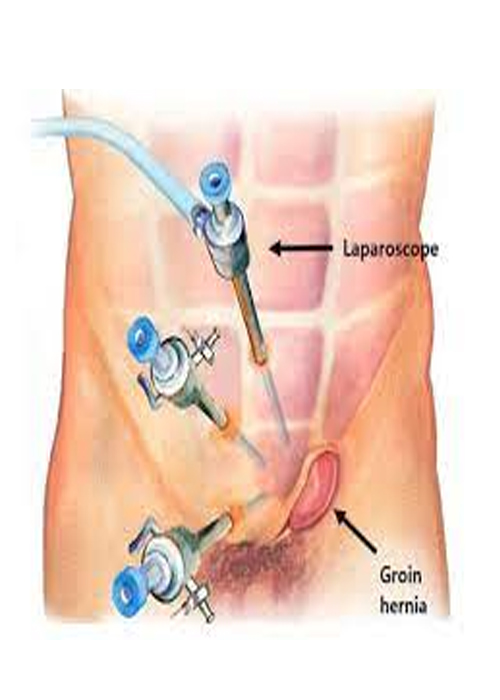
- Laparoscopic Repair: A
minimally invasive approach where small incisions are made, and a camera and
surgical instruments are used to repair the hernia with the help of a mesh.
Benefits of Surgery
- Relief of Symptoms: Surgery
can alleviate pain, discomfort, and the risk of complications associated with
inguinal hernias.
- Prevention of Complications:
By repairing the hernia, the risk of incarceration (where the hernia becomes
trapped) or strangulation (where the blood supply to the trapped tissue is cut off)
is significantly reduced.
- Improved Quality of Life:
Patients often experience improved physical comfort and functionality after hernia
repair, allowing them to resume normal activities without the limitations imposed by
the hernia.a.
Risks and Expectations
- Surgical Risks:
Potential risks of surgery include infection, bleeding, damage to nearby structures
(such as nerves or blood vessels), and recurrence of the hernia.
- Recovery:
Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery (open vs. laparoscopic) and
individual factors. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few weeks to
a couple of months after surgery.
- Recurrence: Although surgical
repair is usually successful, there is a small risk of the hernia recurring,
especially if the repair was complex or if the patient has risk factors such as
obesity or chronic cough.
- Long-Term Outlook: With
successful surgery and appropriate post-operative care, the outlook for patients
with inguinal hernias is generally good. Following medical advice regarding
lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding heavy lifting and maintaining a healthy
weight, can help reduce the risk of recurrence and promote long-term well-being.